Your Cart is Empty
August 12, 2021 4 min read

Take our quiz and find which supplements your body is craving.

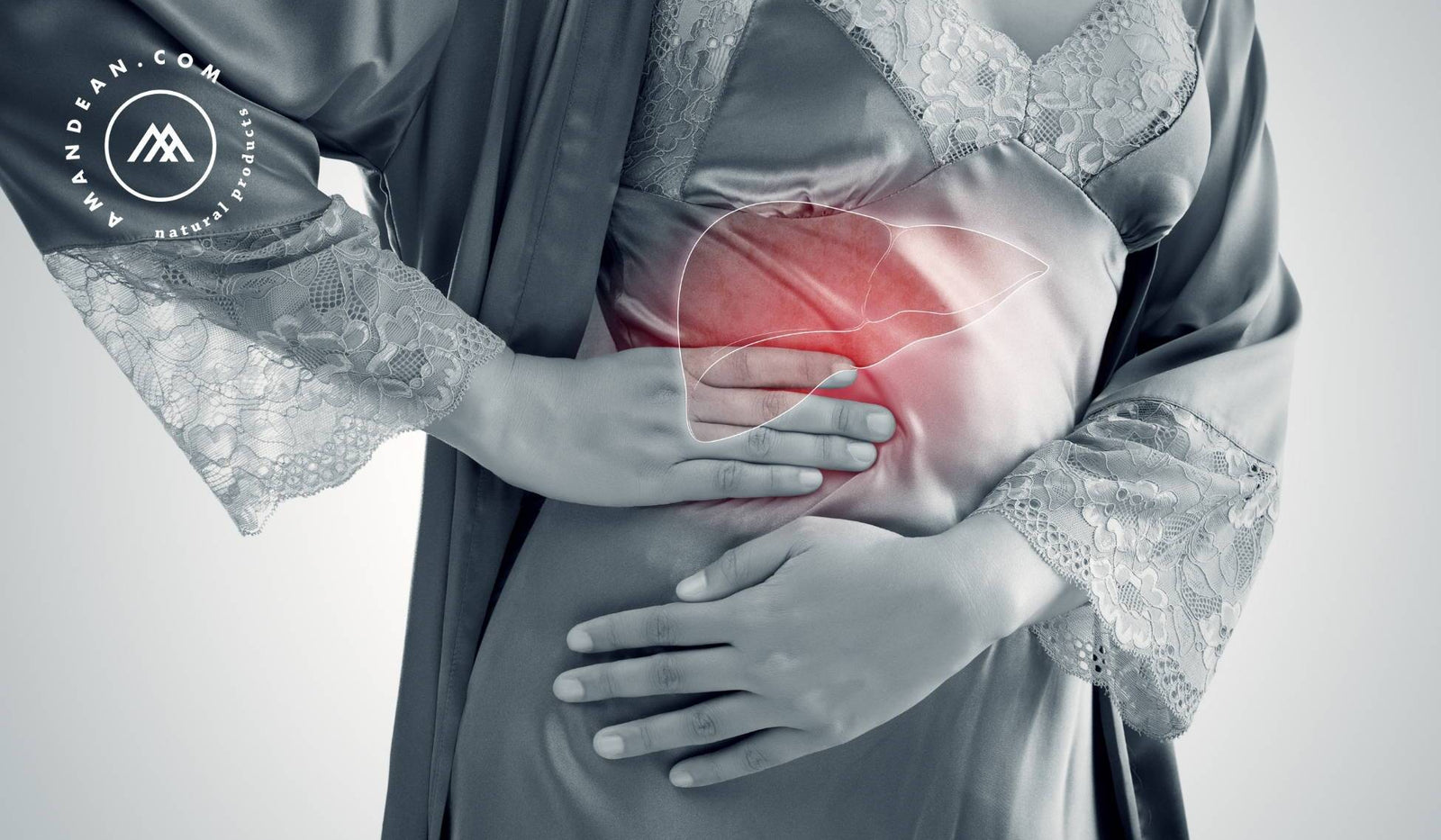
Glutathione (GSH), pronounced “GLOO-tuh-thay-ohn,” is a very powerful antioxidant. Glutathione is a tripeptide consisting of three amino acids -cysteine, glutamic acid (plus glutamine derived from glutamic acid), and glycine. It can be found in nearly every single cell in the human body. As an antioxidant, glutathione supports your immune system in fighting infections, supports liver function, promotes vital brain functions, fights oxidation from free radicals, helps certain enzymes function, regenerates vitamins C and E, eliminates fat-soluble toxins and heavy metals, and boosts energy from the inside-out. During youth, our levels of glutathione are high and the body has no problems with glutathione synthesis. As we age, however, oxidative damage from toxins, diet, stress, environmental factors, and the aging process inhibits glutathione production. Glutathione deficiency is usually characterized by a reduction in the body's ability to detox, inability to repair DNA, increased cell mutations, increased oxidative stress, and reduced oxygen and nutrients supply to cells. Other than increased inflammation, it's hard to detect glutathione shortage by "feeling" alone. However, due to the deregulation of cells and increased cell death, glutathione deficiency is often observed in those with autoimmune diseases, arthritis, asthma, and even Parkinson's disease.
While a decrease in glutathione levels can result in potential health decline, supplementation can help to increase glutathione levels and help bring our bodies (including the liver) back to glowing health! Oral glutathione supplementation may improve the symptoms of psoriasis, Parkinson's disease, some autoimmune diseases, diabetes (by improving insulin resistance), alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, AND may reduce oxidative damage in children with autism.

Above all, glutathione is commonly used to improve the detoxification process of the liver. Liver disease accounts for approximately 2 million deaths per year worldwide. When glutathione levels and overall antioxidant levels are low, cell death in the liver is expedited and can lead to a number of different liver diseases. Thus, liver detoxification is needed.
The role of the liver is to transform fat-soluble molecules into water-soluble molecules, preparing them for excretion by entering the bloodstream and being removed by the body. Liver detox happens in two phases -- phase I and phase II. During phase I, the liver uses specific enzymes to transform the toxins into less harmful, but nonetheless harmful toxins. Then, phase II is initiated to neutralize and remove the byproducts of phase I detoxification by making the toxins water-soluble. This is done through amino acid conjugation. Glutathione, sulfate, and glycine are the primary molecules responsible for this process.
Low levels of glutathione can result in both alcohol and non-alcohol-induced fatty liver disease. Studies have found that both orally and intravenously administered glutathione has positive effects on individuals with fatty liver disease when paired with proactive lifestyle changes. For instance, in one study participants were given a 300 mg oral dose of glutathione every day for four months. They were also asked to make healthy diet and exercise choices for 3 months during the study. At the end of the study, improved protein, enzyme, and bilirubin levels were measured and glutathione was deemed to have a potential therapeutic effect for those with fatty liver diseases.

Asparagus, avocado, dark leafy greens like spinach and kale, broccoli, and other cruciferous vegetables are common food sources of glutathione. Unfortunately, however, digestive enzymes break these food sources of glutathione down before it can be properly absorbed. Similarly, most oral glutathione supplements don't make it past the stomach acid before they can be properly absorbed by the body. For that reason, liposomal glutathione supplements are recommended.
A liposome is a sphere-shaped vesicle made up of one or more phospholipid bilayers, which resemble the structure of cell membranes. Simply put, they are the most bioavailable formula for our bodies to use effectively because they bypass the digestive system and go directly into the cells. Additionally, consuming other foods like Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, and kale can also provide the three key building blocks (glutamate, cysteine, and glycine) to manufacture glutathione naturally.

As an antioxidant, glutathione supports your immune system in fighting infections, supports liver function, promotes vital brain functions, fights oxidation from free radicals, helps certain enzymes function, regenerates vitamins C and E, eliminates fat-soluble toxins and heavy metals, and boosts energy from the inside-out.
Glutathione deficiency is usually characterized by a reduction in the body's ability to detox, inability to repair DNA, increased cell mutations, increased oxidative stress and reduced oxygen and nutrients supply to cells.
Liposomal glutathione supplements are an effective way to boost your body's natural glutathione production.
Milk thistle extract contains an antioxidant and an anti-inflammatory called silymarin that has been shown to help ease inflammation and promote cell repair within the liver.

October 17, 2025 8 min read
Find out why creatine is better for vegans! Boost your wellness game and unlock peak performance with Amandean's premium supplements today.
October 16, 2025 7 min read
Learn whether collagen in coffee is just another wellness fad. Examine the facts, benefits, and how to use collagen in coffee for beauty and joint support.

September 22, 2025 9 min read
Unlock the full benefits of creatine for women. Boost energy, beauty, and brainpower with Amandean’s clean formulas.