Your Cart is Empty

November 10, 2020 6 min read
There are about 28 known types of collagen in the human body, and more and more benefits are being uncovered almost every day! With all these different types of collagen, and especially when brands use the word "collagen" as an umbrella term, it can be difficult to know what types of collagen you're actually getting and which ones are doing the work!
We know that in general, collagen is the most abundant protein in our bodies and is a building block of our extracellular matrix. Specifically, collagen type I constitutes 80–85% of the dermal ECM, while collagen III constitutes 8–11%. Collagen protein is vital to the health of all the connective tissues, tendons, joints, blood vessels, teeth, and bones in our body.
That's why we start to see almost total-body effects whenever our rates of collagen synthesis begin to drop. Our skin starts to thin, sag, wrinkle, and form cellulite and our joints become worn, causing discomfort and lack of mobility.
Take our quiz and find which supplements your body is craving.


Type III is the second most abundant type of collagen. Type III collagen molecules are made of amino acids, primarily glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline, which form into a triple helix type III procollagen molecule (think of it as a rope with three strands).
Procollagen is then transported through Golgi, bonded, and its amino acids lysine and proline are modified so that it can cross-link between other molecules to form collagen fibrils. Fibrillogenesis occurs when all these fine fibrils come together and begin cross-linking with other molecules to form the strong solid collagen fibers that support your organs, muscles, and connective tissues.
Type III collagen is unique from other types of collagen both in its location and its function. The top three types of collagen all belong to the fibrillar collagen family:


Types I and III collagen are truly the most iconic duo. Studies have even found that type III collagen is an essential component of the type I collagen fibrils. Together, they have the following benefits:
When your body has all the collagen it needs, your skin is firm and fresh, your joints are sturdy and flexible, and the bones in your body are healthy and strong.
However, when the COL3A1 gene (the gene that encodes type III collagen) becomes mutated, it can lead to EDS (Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome type IV) which leaves individuals prone to spontaneous ruptures of bowel and large arteries. Insufficient levels of type III collagen can also lead to wrinkles, hair loss, brittle nails, and stiff joints.
Since collagen is a protein, you can find it in your typical protein-heavy foods such as meats, dairy, fish, and eggs. Vitamin C and the minerals zinc, manganese, and copper can also boost collagen synthesis so make sure to plan your weekly dinners to include lots of citruses, grains, green veggies like brussels sprouts and broccoli, and nuts.
Wherever your diet falls short, collagen supplements can be added! There are many different kinds of collagen products on the market from creams to supplements. Here are a few things to keep in mind to choose the best supplements for your muscles, hair, skin and nails.
Even though collagen is synthesized naturally in the body, our collagen production drops by about 1.5% a year after the age of 30. Your body's collagen can also become damaged by vitamin C deficiencies, autoimmune diseases that attack your body's protein, and bacteria such as the enzyme collagenase. This is where supplements come into play!

Collagen peptides from grass-fed cows are a great source of types I and III collagen. Just make sure it's free of additives and is hydrolyzed so it can be absorbed and used by the body more efficiently! Both gelatin and grass-fed collagen peptides contain collagen types I and III.
Outside of supplements, bone broth soups are one of the few dishes that contain beef gelatin. However, powdered beef gelatin supplements can be added to many dishes like pumpkin pie or fruit gummies to add a little extra spring to your meal and type III collagen in your gut! Lastly, marine collagen is another excellent source and contains even more type 3 collagen (approx. 10%).
It is also a popular choice for pescatarian diets. Marine collagen is the most bioavailable collagen supplement on the market and is easy to incorporate into your daily meals and cups of coffee to support your hair, skin, nails, and muscles.
These supplements heal the skin, hair, and nails from the inside out. However, there are also plenty of collagen creams to fight your skin’s natural signs of aging. Just remember to pair them with a scoop of collagen a day to keep the wrinkles away. If you need help choosing between marine collagen and grass-fed collagen peptides, just reach out to our product experts!
Type III is the second most abundant type of collagen.
Type III collagen molecules are made of amino acids, primarily glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline.
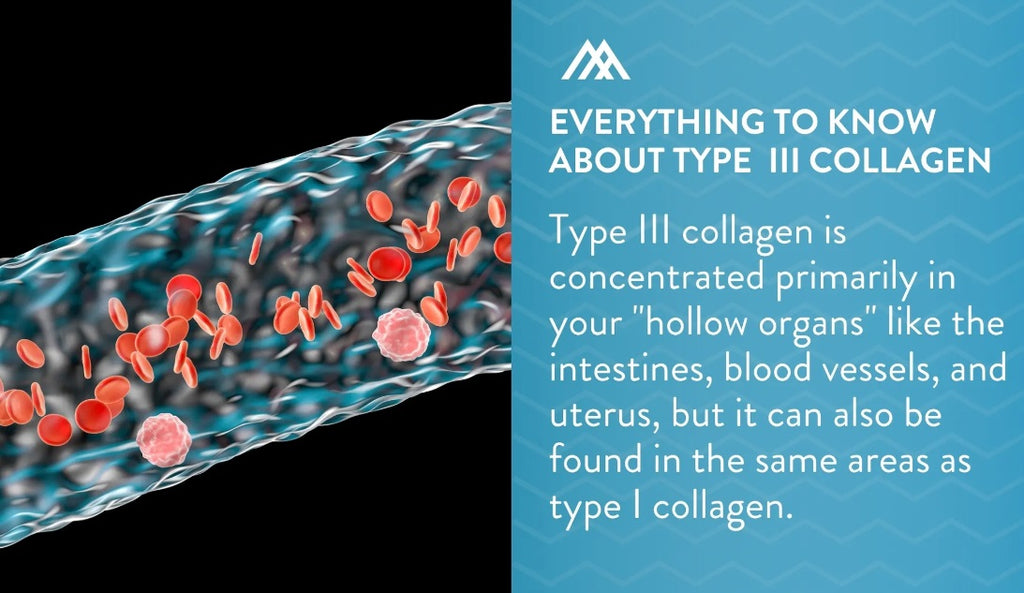
Type III collagen is concentrated primarily in your "hollow organs" like the intestines, blood vessels, and uterus, but it can also be found in the same areas as type I collagen.
Type III collagen is uniquely integral for supporting the arterial walls, making it key for cardiovascular health.
Type III collagen supplementation may also help IBS sufferers by strengthening the intestine walls and helping to manage inflammation.

October 17, 2025 8 min read
Find out why creatine is better for vegans! Boost your wellness game and unlock peak performance with Amandean's premium supplements today.
October 16, 2025 7 min read
Learn whether collagen in coffee is just another wellness fad. Examine the facts, benefits, and how to use collagen in coffee for beauty and joint support.

September 22, 2025 9 min read
Unlock the full benefits of creatine for women. Boost energy, beauty, and brainpower with Amandean’s clean formulas.